lv segments | ncdr coronary artery segment diagram lv segments Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the . View and Download DMP Electronics DualCom Series programming and installation manual online. DualCom Series measuring instruments pdf manual download.
0 · ncdr coronary artery segment diagram
1 · Lv wall segments echo
2 · Lv segments echo
3 · Lv segments diagram
4 · 17 wall segments echo
5 · 17 segments of the heart
6 · 17 segments of left ventricle
7 · 16 segment Lv model
Draugiem.lv ir Latvijas pirmā un populārākā pašmāju sociālā tīkla vietne. Reģistrējies, veido draudzīgas saites un izmanto citas portāla sniegtās iespējas.
ncdr coronary artery segment diagram
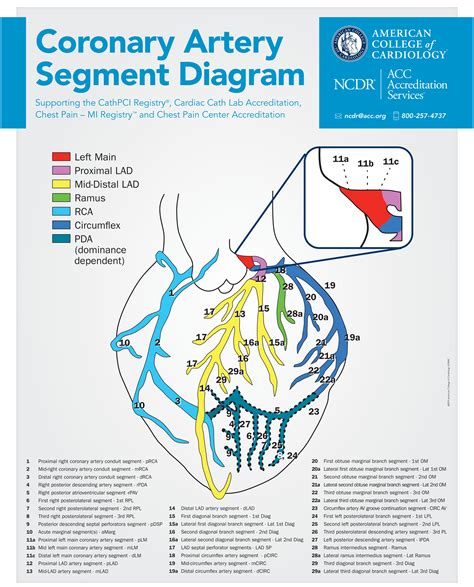
The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as . Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the 4 walls were divided into 17 .LV segmental anatomy. The regional distribution of myocardial ischemia can be detected as segmental LV wall motion abnormalities by TEE. The entire LV in the 17-segment model can .
Left ventricle | Radiology Reference Article - Radiopaedia
Lv wall segments echo
Lv segments echo
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the . phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA passively fills LV and then stops), atrial contraction; diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling .A line, drawn from the base to the myocardial wall, in diastole, will cross each of the parts of the suspension unit. All of the parts of the suspension unit are involved in the contraction process. .
Assessment of the size, mass, geometry, and function of the left ventricle is fundamental for the diagnosis and prognosis of most cardiac diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart .
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease: guiding management and predicting outcomes. Numerous echocardiographic .Segments of the left ventricle. Based on anatomical landmarks and autopsy studies (Edwards et al), the left ventricle is divided into three equal parts along the long axis of the ventricle. This creates three circular sections of the left ventricle named basal, mid-cavity, and apical.The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as segment 17. The 17 segments correspond to specific coronary artery territories (1) .
Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the 4 walls were divided into 17 segments: 6 basal, 6 mid, 4 apical, and 1 segment being the apex (Figure 2).LV segmental anatomy. The regional distribution of myocardial ischemia can be detected as segmental LV wall motion abnormalities by TEE. The entire LV in the 17-segment model can be imaged in long-axis using a combination of the TEE mid-esophageal four-chamber view (a), TEE mid-esophageal two-chamber view (b), and TEE mid-esophageal long-axis .
hermes birkin 30 black ghw
Left ventricle | Radiology Reference Article - Radiopaedia
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each . phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA passively fills LV and then stops), atrial contraction; diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling where LV is unable to fill to a normal LVEDV without an increase in end-diastolic pressure.A line, drawn from the base to the myocardial wall, in diastole, will cross each of the parts of the suspension unit. All of the parts of the suspension unit are involved in the contraction process. Disruption of any of these segments may affect the contraction of the heart.Assessment of the size, mass, geometry, and function of the left ventricle is fundamental for the diagnosis and prognosis of most cardiac diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, structural heart disease, etc.
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease: guiding management and predicting outcomes. Numerous echocardiographic techniques, including left ven-tricular ejection fraction, are used in routine clinical practice to assess left ventricular systolic function.Segments of the left ventricle. Based on anatomical landmarks and autopsy studies (Edwards et al), the left ventricle is divided into three equal parts along the long axis of the ventricle. This creates three circular sections of the left ventricle named basal, mid-cavity, and apical.
The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as segment 17. The 17 segments correspond to specific coronary artery territories (1) . Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the 4 walls were divided into 17 segments: 6 basal, 6 mid, 4 apical, and 1 segment being the apex (Figure 2).LV segmental anatomy. The regional distribution of myocardial ischemia can be detected as segmental LV wall motion abnormalities by TEE. The entire LV in the 17-segment model can be imaged in long-axis using a combination of the TEE mid-esophageal four-chamber view (a), TEE mid-esophageal two-chamber view (b), and TEE mid-esophageal long-axis .
Left ventricle | Radiology Reference Article - Radiopaedia
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .
phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA passively fills LV and then stops), atrial contraction; diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling where LV is unable to fill to a normal LVEDV without an increase in end-diastolic pressure.A line, drawn from the base to the myocardial wall, in diastole, will cross each of the parts of the suspension unit. All of the parts of the suspension unit are involved in the contraction process. Disruption of any of these segments may affect the contraction of the heart.
Assessment of the size, mass, geometry, and function of the left ventricle is fundamental for the diagnosis and prognosis of most cardiac diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, structural heart disease, etc.
Lv segments diagram
Reģistrēties. Ikvienam draugiem.lv lietotājam ir jānorāda savs īstais vārds un uzvārds. Ievietojot bildi, tajā ir jābūt redzamam tev. Šo noteikumu neievērošanas gadījumā tiks bloķēta pieeja draugiem.lv portālam bez brīdinājuma. Tavs telefona numurs * Uz norādīto numuru mēs nosūtīsim reģistrācijas kodu, kurš būs .
lv segments|ncdr coronary artery segment diagram