lv freewall thickness echocardiography | left ventricular thickness chart lv freewall thickness echocardiography tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations. On March 25th, 1998, Omega released the Speedmaster Professional X-33 reference 3290.50. Indeed, this digital Speedmaster Professional (mind the “Professional”) was qualified by NASA for use on Space Shuttle missions. Speedmaster LCD History.
0 · normal left ventricular wall thickness
1 · left ventricular thickness normal range
2 · left ventricular thickness mri
3 · left ventricular thickness chart
The Rolex Submariner Date 116610 is fitted with the certified chronometer in-house .
normal left ventricular wall thickness
tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations.wall thickness. LV hypertrophy, although usually asymmetric,can also be concen-tric. The distribution of hypertrophy can be in any pattern and at any location, including the right .
nike 270 maat 38
Increased left ventricular myocardial thickness (LVMT) is a feature of several cardiac diseases. The purpose of this study was to establish standard reference values of . The first and most commonly used echocardiography method of LVM estimation is the linear method, which uses end-diastolic linear measurements of the interventricular . Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for .
Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six . Echocardiography offers a reliable and reproducible method for measuring left ventricular wall thickness and mass. Finally, ultrasound may provide an accurate method for .
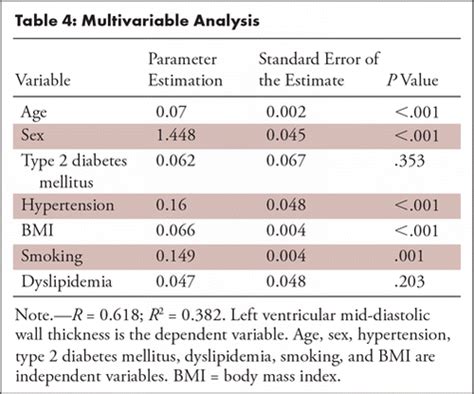
Recommendations: Abnormal RV wall thickness should be reported, if present, in patients suspected of having RV and/or LV dysfunction, using the normal cutoff of 0.5 cm from either PLAX or subcostal windows .LVM and RWT. LVM is the acronym for Left Ventricular Mass. LV mass (LVM) is a vital prognostic measurement we obtain with echocardiography to manage hypertension. RWT is the acronym for Relative Wall Thickness and is an .Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women). Refer to Table 2 (normal values for non-contrast images) and Table 4 (recommendations for the normal
tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations.wall thickness. LV hypertrophy, although usually asymmetric,can also be concen-tric. The distribution of hypertrophy can be in any pattern and at any location, including the right ventricle. Although septal predominance is more common, hypertrophy can be isolated to the LV free wall or apex (Figure 1). Thepresence of hypertrophy localized to . Increased left ventricular myocardial thickness (LVMT) is a feature of several cardiac diseases. The purpose of this study was to establish standard reference values of normal LVMT with cardiac magnetic resonance and to assess variation with image acquisition plane, demographics, and left ventricular function. The first and most commonly used echocardiography method of LVM estimation is the linear method, which uses end-diastolic linear measurements of the interventricular septum (IVSd), LV inferolateral wall thickness, and LV internal diameter derived from 2D-guided M-mode or direct 2D echocardiography. This method utilizes the Devereux and Reichek .
Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for therapy. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view.Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six segments of 60° each. Echocardiography offers a reliable and reproducible method for measuring left ventricular wall thickness and mass. Finally, ultrasound may provide an accurate method for measuring systolic wall thickening in man.Recommendations: Abnormal RV wall thickness should be reported, if present, in patients suspected of having RV and/or LV dysfunction, using the normal cutoff of 0.5 cm from either PLAX or subcostal windows .
LVM and RWT. LVM is the acronym for Left Ventricular Mass. LV mass (LVM) is a vital prognostic measurement we obtain with echocardiography to manage hypertension. RWT is the acronym for Relative Wall Thickness and is an additional reference value that can help further classify the .Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women). Refer to Table 2 (normal values for non-contrast images) and Table 4 (recommendations for the normaltricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations.
wall thickness. LV hypertrophy, although usually asymmetric,can also be concen-tric. The distribution of hypertrophy can be in any pattern and at any location, including the right ventricle. Although septal predominance is more common, hypertrophy can be isolated to the LV free wall or apex (Figure 1). Thepresence of hypertrophy localized to . Increased left ventricular myocardial thickness (LVMT) is a feature of several cardiac diseases. The purpose of this study was to establish standard reference values of normal LVMT with cardiac magnetic resonance and to assess variation with image acquisition plane, demographics, and left ventricular function. The first and most commonly used echocardiography method of LVM estimation is the linear method, which uses end-diastolic linear measurements of the interventricular septum (IVSd), LV inferolateral wall thickness, and LV internal diameter derived from 2D-guided M-mode or direct 2D echocardiography. This method utilizes the Devereux and Reichek . Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for therapy. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view.
Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six segments of 60° each. Echocardiography offers a reliable and reproducible method for measuring left ventricular wall thickness and mass. Finally, ultrasound may provide an accurate method for measuring systolic wall thickening in man.Recommendations: Abnormal RV wall thickness should be reported, if present, in patients suspected of having RV and/or LV dysfunction, using the normal cutoff of 0.5 cm from either PLAX or subcostal windows .
left ventricular thickness normal range
left ventricular thickness mri
maat 21 nike
left ventricular thickness chart

$13K+
lv freewall thickness echocardiography|left ventricular thickness chart